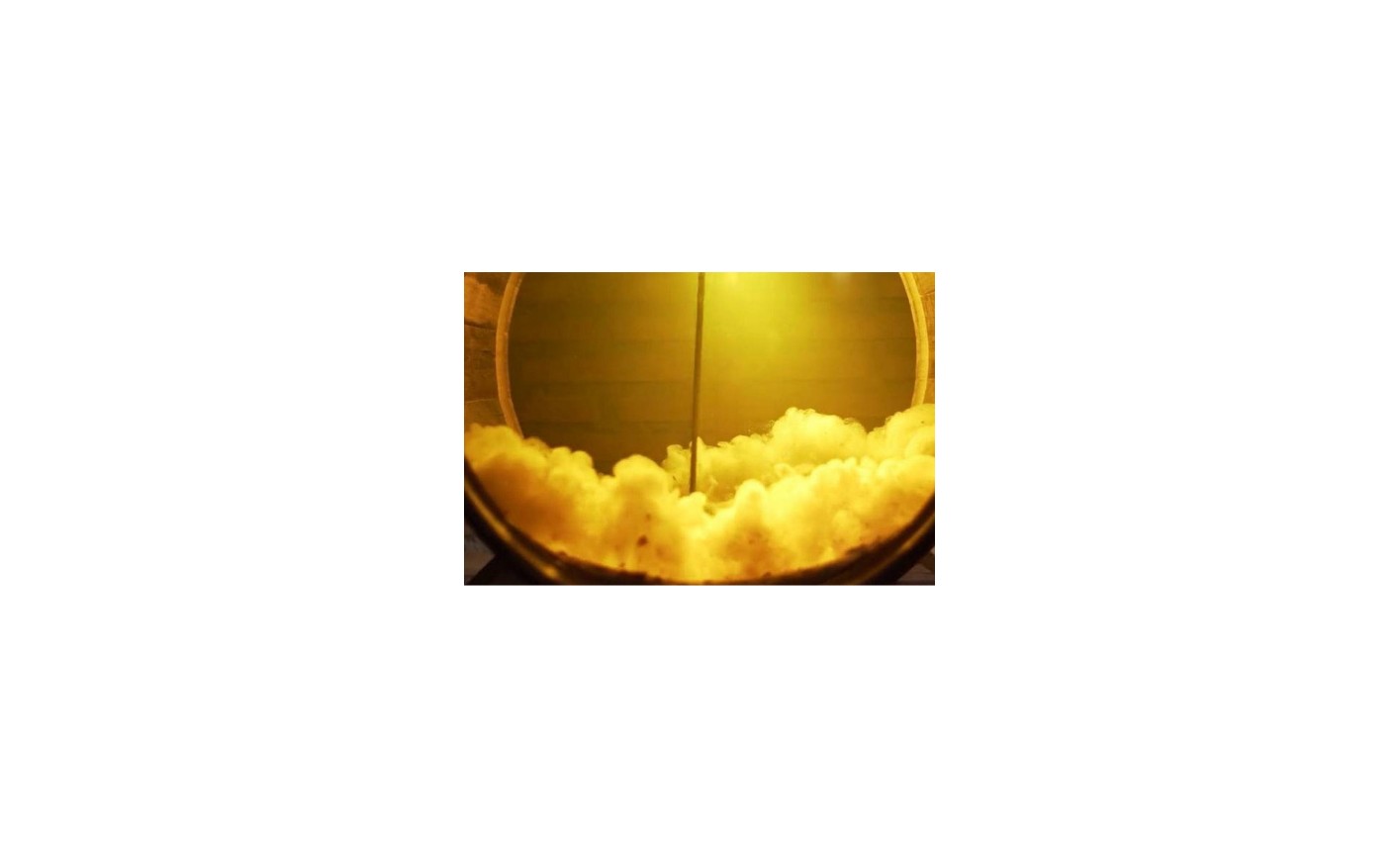

It is the result of a completely natural process in which the solid matter is deposited in the barrel during the fermentation of the wine.
It is made up of dead yeasts and the remains of the grapes themselves. Aging on lees not only helps the wine aging, but also enriches it and gives it smoothness in a natural way.

WHAT ARE THEY USED FOR?
Those compounds that we have named you before are very interesting for wine and each one has a function. They add complexity to the wine, give it smoothness and richness. They also help the aging of the wines. That is why we are interested in the lees, at least what we call the fine lees, remain in the wine and somehow enrich it in a natural way.
WHAT WINES FOR?
Well, nowadays it is used for both whites and reds: For white wines, provided that they are fermented in barrels and sometimes so that those that even ferment in tanks want to add more complexity and more life. White wines on lees are more intense and can also be kept for longer. It has also been incorporated into young red wines to give them a little more volume in the mouth and make them rounder.
HOW DOES IT WORK WITH THE LINES?
In order for the lees to yield all those rich compounds to the wine, it is necessary to try to put them in suspension and that they remain in contact with the wine for as long as possible. So we do a technique that we call battonage, which consists of shaking the lees with a kind of metal stick so that when stirred, they come into contact with the wine and give it their compounds. After a few hours, the mothers are deposited again and that is why they must be shaken periodically.
HOW MUCH DO WE BATTLE?
Here each teacher has his booklet. And since it is a manual thing, the winery's budget also commands, but the ideal is to do it once a day, at the beginning of the aging, then two or three times a week and at the end once a week.
BENEFITS:
- Naturally protects wine against oxidation.
- Prevents solid substances from precipitating and forming deposits.
- It favors its integration and volume.
- It provides pleasant aromas and intensifies those of the grape.
- Provides stability and coloration.


